Improving Diabetic Care: A Guide to Diabetic Retinal Screenings
According to the National Eye Institution, diabetic retinopathy is the most common form of diabetic eye disease and is the leading cause of blindness in adults ages 20 to 74. It affects over 7.7 million Americans, with cases expected to increase to more than 14.6 million by 2030.
Less than 50% of diabetic patients receive their annual diabetic retinopathy eye screening, which has resulted in a huge care gap. Untreated late-stage diabetic retinopathy causes blindness, and once vision is lost due to DR, it is nearly impossible to be restored. However, if diabetic retinopathy cases are caught in their mild stages through early detection, patients can receive effective treatment and prevent potential vision loss. Early detection and treatment alone can reduce a patient’s risk of blindness by 95%.
In this article, we are covering key insights providers should consider when looking into integrating diabetic retinal screenings into their offerings, as well as some best practices for administering the exam.
What is a Diabetic Retinal Screening and How Does It Work?
A diabetic retinal screening is the imaging of the blood vessels within the retina to detect diabetic retinopathy in diabetic patients. This process can be seamless and simple by choosing equipment that matches your organization’s workflow needs and environment.
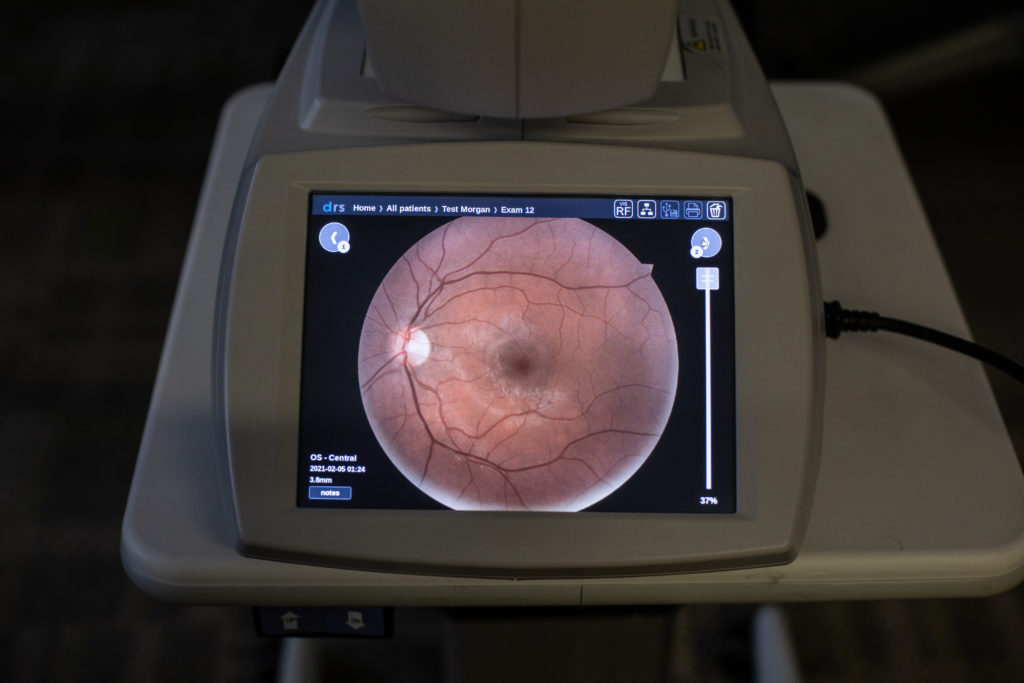
The point-of-care diabetic retinal screening process uses non-mydriatic fundus cameras which means pupil dilation is not required. The administrator will use the fundus camera to take images of the back of a patient’s eyes (retina). The images are reviewed by a licensed eye care provider to check for diabetic retinopathy.

Organizations using IRIS, securely upload the fundus images to the cloud-based grading platform. From there, a licensed eye care provider from the IRIS Reading Center (IRC) will provide a diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy, if any, including the level of severity. IRIS’s proprietary image enhancement software is automatically applied to every image before the diagnosing provider receives them. The ability to review enhanced and original images improves the likelihood that IRC physicians will be able to see any pathology that is present. The IRIS solution allows providers and patients to implement treatment options before patients reach the point of permanent or total vision loss.
Depending on the results of the diabetic retinal screenings, the ordering provider may begin helping their patients seek appropriate treatment as soon as possible to prevent blindness and vision loss.
The Four Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy has different stages that classify severity. Below is a quick refresher on the four main stages:
1. Mild NPDR
In the mild stage of diabetic retinopathy, balloon-like swelling (microaneurysms) in the retina will likely be present. . This stage rarely affects vision or needs treatment, but does signal that diabetes has begun impacting the eyes and that there is an increased risk of disease progression.. At this stage, it’s advised that the patient begins to take steps to better control their blood sugar and diet to reduce progression.
2. Moderate NPDR
The moderate stage of diabetic retinopathy is marked by damage to some of the blood vessels in the retina where there is leakage of blood and fluid into the retina tissue. The fluid can cause vision loss.
3. Severe NPDR
In this stage, increased leakage of blood and fluid into the retina will likely cause noticeable changes in vision. Patients with severe retinopathy will need to receive treatment as soon as possible. Sometimes damage can still be reversed at this stage with appropriate treatment.
4. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
At this point, the disease has advanced significantly and is very threatening to the patient’s vision. Due to the damage to the eyes’ blood vessels, there is poor circulation inside the eye, which can eventually lead to blindness. At this stage, patients require immediate referral to a retina specialist for further examination and treatment.
Common Treatment Plans for Diabetic Retinopathy
The best way to prevent noticeable vision loss from diabetic retinopathy is through early detection by annual diabetic retinal screenings. As a healthcare organization, providing quality care is always top of mind, and delivering on that front means optimizing workflows and staff experience. Having a top-of-the-line diabetic retinopathy solution can improve both patient and organizational outcomes.
If diabetic retinopathy is detected after a screening, treatment options are the next step. Below are several types of diabetic retinopathy treatments depending on the level of severity:
1. Blood Sugar Control
In early diabetic retinopathy, additional treatment may not be necessary yet. However, good blood sugar control is always important and can sometimes slow DR progression.
2. Injections
This treatment is more common for patients with advanced diabetic retinopathy. Medications called vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors can be injected into the eye and help stop the growth of new blood vessels while decreasing fluid buildup.
Learn more about injections to treat diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema here.
3. Laser Treatments
There are two types of laser treatments that can be performed for those with more severe cases of diabetic retinopathy:
-
-
-
- Photocoagulation: Also known as focal laser treatment, this type of procedure is performed to stop or slow the leakage of blood and fluid in the eye.
- Panretinal photocoagulation: Also known as scatter laser treatment, this procedure is performed to shrink abnormal blood vessels.
-
-
4. Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is a procedure where tiny incisions are made into the patient’s eyes to remove scar tissue and blood from the center of the eye. It’s performed in a surgery center or hospital, as anesthesia is required.
Each of these treatments can help slow or sometimes even stop the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Regardless of whether treatment is administered, vision loss may still be possible, as diabetes is a lifelong condition.
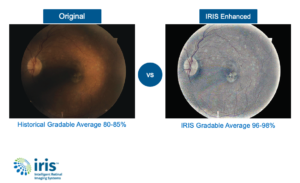
The IRIS Difference
Conclusion: Achieve Better Diabetic Patient Care with Increased Availability to Diabetic Retinopathy Screenings
As healthcare providers consider the advantages of offering diabetic retinal screenings to patients, solutions such as IRIS provide the best experience for both the patients and providers. The IRIS solution can provide early detection capabilities for any type of healthcare organization with diabetic patients, creating a simple process for providers while offering availability for patients to stay on top of their total diabetic health plan.
Connect with us to learn more about how you can provide more accessible screening solutions for your patients today.
SM 117 Rev A
Get started with IRIS today.
Want to know if IRIS is right for you? Schedule a one-on-one consultation with our team. We’re here to help.