HEDIS Compliance: Why and How Exceeding HEDIS Measures is Vital for Your Practice

Since 1991, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have used the Health Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS) to coordinate coverage changes that affect insurance coding and patient care. HEDIS is an integral tool to oversee healthcare in the United States. However, staying on top of HEDIS changes can be a challenge for healthcare providers.

What Is the Purpose of HEDIS?
The Health Effectiveness Data and Information Set, or HEDIS, is a set of standardized performance measures managed by the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA). The measures are to evaluate insured patients’ quality of care and services.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) contracted the NCQA to create a five-star quality rating system to gauge how well providers and health plans deliver care, with a rating of five being excellent and one being poor. The CMS HEDIS standards also measure the effectiveness of special needs plans (SNPs) addressing common public health issues like asthma, cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and more.
What Are HEDIS Measures?
You might be wondering, “What are HEDIS measures?”. HEDIS assesses the quality of healthcare plans based on over 90 measures across six domains of care:
- Effectiveness
- Availability
- Experience
- Utilization/risk-adjusted utilization
- Health plan descriptive information
- Measures reported using electronic clinical data systems.
These measures allow HEDIS to evaluate the quality of services, compare performance from plan to plan, and make adjustments based on identified areas of improvement.

As of now, 90% of Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial health plans in the US participate in HEDIS review by submitting medical records, administrative data, and other supplemental information. By reviewing medical data, HEDIS can assess how healthcare plans and practices are meeting benchmarks for care delivery.
Why Is HEDIS Important?
HEDIS’ primary purpose lies in improving preventative care. Preventative care, including routine screenings for common medical conditions, results in better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
HEDIS aims for providers and insurers to achieve compliance in all six domains of care.
CMS offers pay-for-performance incentives to participating organizations that are meeting standards of care. CMS defines these incentives as “the use of payment methods and other incentives to encourage quality improvement and patient-focused high-value care.”
HEDIS in Healthcare for Diabetic Care
Managing diabetes and preventing complications from diabetes is a growing priority within the healthcare community. The prevalence of diabetes in the United States is evident, though its harmful side effects are often understated. In 2021, 37.3 million people in the United States had diabetes, with 8.5 million undiagnosed.
Furthermore, of US adults aged 18 or older, 96 million were diagnosed with pre-diabetes, equaling 38% of the adult population.

Source: Centers for Disease Control (CDC.gov)
Diabetes complications can result in anemia, kidney disease, high blood pressure, and diabetic retinopathy, with the latter most often leading to blindness if it isn’t diagnosed and treated early on.
HEDIS has developed guidelines to manage diabetes care in order to prevent related illnesses. One primary tactic for diabetes management is careful monitoring, typically performed during yearly exams. These comprehensive diabetic care benchmarks seek to minimize diabetes-related complications.
HEDIS-compliant comprehensive diabetic care standards suggest that US adult diabetics ages 18-75 should undergo annual screenings, including:
- Hemoglobin A1c testing
- Retinal eye exam
- Nephropathy (kidney disease monitoring)
- Blood pressure control
Multiple factors can play into an organization’s HEDIS compliance scores, including easy access to testing for patients, the effectiveness of the testing itself, and a patient’s care experience with their primary medical physician.
HEDIS Measures for Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR), a complication of diabetes, is characterized by damage to the small blood vessels present in the retina, usually due to high blood sugar levels. DR can come in two main stages: non-proliferative DR, which can cause slight blurring of vision, or proliferative DR, which can lead to complete vision loss.
4.2 million adults were diagnosed with DR in the US alone, with around 655,000 individuals having vision-threatening DR. Moreover, diabetes-related complications are now the leading cause of blindness among adults aged 18-64 years of age. However, negative outcomes from diabetic retinopathy are largely preventable through careful disease monitoring, including yearly retinal exams.
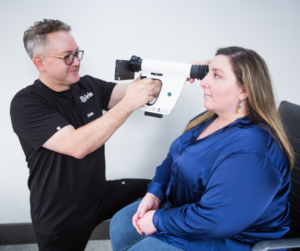
HEDIS compliance measures for comprehensive diabetic care include a retinal eye exam in the current year by an eye care professional — an ophthalmologist or optometrist. These exams can include remote interpretation solutions suited for point-of-care implementations. This allows primary care providers and other healthcare entities to offer retinal screenings so patients don’t need to schedule a separate specialist visit.
Adding HEDIS-compliant retinal screening capabilities in primary care and clinic settings increases patient access to diabetic retinopathy screenings and boosts provider HEDIS ratings.
IRIS For HEDIS Compliance
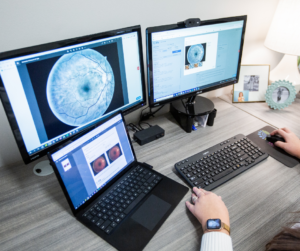
The IRIS solution provides retinal screenings without the need for a dilated eye exam by an ophthalmologist. IRIS integrates with retinal camera systems to capture images of a patient’s retina. The system automatically and securely uploads images, which undergo enhancement to create a color-contrasting view of the retina.
After IRIS-trained staff performs a retinal exam, images are uploaded directly to the IRIS cloud. These enhanced images allow our IRIS Reading Center (IRC) board-certified eye care professionals to accurately review and diagnose the presence of diabetic retinopathy or macular edema, as well as its severity. These providers can also document the suspicion of many other retinal diseases commonly found in diabetic patients, such as glaucoma, cataracts, wet and dry AMD, and others.
Retinal imaging cameras can be integrated into primary care settings and clinics or by mobile healthcare providers.
This allows providers to offer HEDIS-compliant diabetic retinopathy screenings during routine medical appointments, which increases patient access to screenings. As a result, providers can report with certainty that patients have received screenings as part of their diabetic care.
It is a win-win approach for both patients and practices— quality care is easily administered to patients while practices meet HEDIS requirements and receive financial compensation for doing so.
IRIS technology increases the ease of access to retinal exams for patients, encouraging greater willingness to complete them and, in turn, improves your practice’s HEDIS compliance measures.
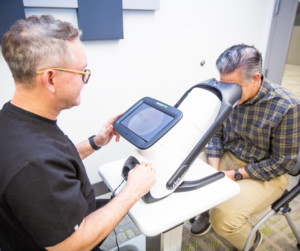
Is IRIS Right for You?
Diabetes is one of the most prevalent health issues in the United States, and as the diabetic population grows, undiagnosed cases of diabetic retinopathy continue to threaten the vision of adults across the country. According to the CDC, more than one in ten Americans have diabetes.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) states, “[the data] show an alarming increase of diabetes in our nation among young adults,” while the high number of unknown pre-diabetics “is fueling the diabetes epidemic.”
All patients with diabetes and pre-diabetes should receive yearly retinal examinations to prevent the progression of diabetic retinopathy. However, only 40-50% of the diabetic population follow through with them annually.
This is a negative outcome for patients and providers alike. As one of the primary HEDIS compliance measures for comprehensive diabetic care, we need innovative solutions to ensure that all diabetic patients complete their annual retinal exams.
IRIS allows practices to do just that by implementing diabetic retinal examinations to eliminate the need for patients to book follow-up appointments or travel to see specialists. In addition, IRIS professionals provide exam results quickly, allowing your practice to easily reach HEDIS standards while providing better quality, convenient care for your patient population.
Still, it is crucial to know how IRIS can fit into your organization. Use our return on investment calculator here to understand how IRIS can benefit your practice.
As you seek solutions to improve your practice’s HEDIS compliance ratings, reach out to us for more information on how IRIS can be integrated into your organization to work towards all-inclusive and successful diabetic care.
FAQs
What quality measures are relevant to diabetes?
HEDIS measures for diabetes are:
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing.
- HbA1c poor control (>9.0%).
- HbA1c control (<8.0%).
- Eye exam (retinal) performed.
- Medical attention for nephropathy.*
- BP control (<140/90 mm Hg).
What is the HEDIS A1C for diabetes?
HEDIS considers HbA1c >9.0% as poorly controlled and HbA1c <8.0% as controlled.
What is the HEDIS measure for HbA1c poor control?
HEDIS considers HbA1c >9.0% as poorly controlled.
What CMS domain does HEDIS fall under?
CMS contracts with the National Committee for Quality Assurance to develop HEDIS measures.
How does CMS collect data for star and HEDIS ratings?
NCQA collects a portion of HEDIS data directly from health plans and preferred provider organizations (PPOs) through the Healthcare Organization Questionnaire. In addition, it collects non-survey data through the Interactive Data Submission System.
SM 112, Rev B
Get started with IRIS today.
Want to know if IRIS is right for you? Schedule a one-on-one consultation with our team. We’re here to help.